introduction
Toys are indispensable playmates for children's growth. With the continuous change of social development and consumer demand, toy types are more developed from traditional toys to electronic toys. Electric toys generally use dry batteries (not button batteries) and button batteries, among which button batteries have the advantages of small size and good electrical performance. Toy products often use button batteries to trigger some simple lighting functions, such as plush toys, toy cars, game consoles, yo yos and music books.
What is button battery
Button battery is a kind of flat small circular single battery with height less than diameter. According to the electrochemical type, it can be divided into non lithium button cells (such as LR44 alkaline button cells) and lithium coin cells (Coin Cells, such as CR2032 lithium manganese button cells).
Button batteries are small in size, with a maximum diameter of 32mm and a thickness of 1mm to 11mm. For example, the LR44 button battery in the example has a diameter of 11.6 mm and a thickness of 5.4 mm; CR2032 lithium manganese coin battery has a diameter of 20 mm and a thickness of 3.2 mm. It is widely used in various consumer goods and household products, such as toys, clocks, calculators, car keys, cameras, electronic scales and music greeting cards.
Danger of button battery
Although button batteries are so widely used, they pose serious and even fatal risks to young children, especially children under 5 years old. Because children's oesophagus is narrow, and it is easier to put small objects into their mouth, ears and nose.
Because of its small size, button batteries can easily be swallowed into children's esophagus or placed in other parts of the body. In addition to the risk of suffocation caused by being stuck in the throat, the button battery staying in the body will immediately trigger the current due to contact with saliva or other body fluids, which will cause chemical reactions, and eventually cause serious burns to the children's esophagus, internal organs or other important organs. The button battery placed in the body may cause serious injury or even endanger life within 2 hours at the earliest. In addition, once the body organs are burned, even if the battery is removed from the body in time, the damage to the body may not stop immediately, but requires surgery and treatment that lasts for many years.
In China and around the world, there have been many cases of serious bodily injury or even death caused by children accidentally placing or swallowing button batteries. There was a news report in China that a 3-year-old child inserted a button battery into the nasal cavity for 3 days. The nasal mucosa was severely burned due to the leakage of strong corrosive battery solution; Another 4-year-old child was found to have a button battery in his eyes. When he took it out, the battery was corroded and fell off.
In addition, a 2-year-old British child died after swallowing the button battery of the remote control. According to the data of the Australian Fair Competition and Consumer Council (ACCC), on average, one child in Australia suffers serious injuries due to swallowing or placing button batteries in one month, and some injuries may even affect his life.
Control requirements of national toy standards
In view of the risks of button batteries, button batteries in toy standards of various countries also have relevant standard requirements for control.
GB 19865-2005 Safety of Electric Toys
The standard requires that button battery and R1 battery shall be untouchable without tools, unless the cover of the battery room can only be opened when at least two independent actions are applied at the same time. In addition, the battery of toys intended for children under three years of age should not be removed without tools, unless the protection of the battery room cover is sufficient.
American ASTM F963-17 toy safety standard
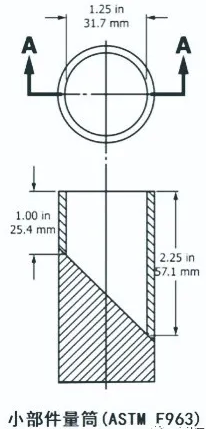
The standard requires that the battery (such as button battery with a diameter less than 31.7 mm) that can be completely put into the measuring cylinder of small parts as shown in the right figure shall be untouchable before and after a series of abuse tests (such as drop, torque, tension, pressure tests, etc.) specified in the standard without hard money, screwdriver or other tools; At the same time, all batteries intended for use by children under three years of age should be untouchable before and after a series of abuse tests according to the standard.
IEC 62115: 2017, EU EN IEC 62115: 2020+A11 and Australian AS/NZS 62115: 2018 Safety Standard for Electric Toys
According to the requirements of the standard, for the battery that can be completely put into the measuring cylinder of small parts or the parts containing the battery, before and after the abuse test specified in the standard, if no tools are used, the battery shall be inaccessible or removed; For other batteries, they shall not be removed without tools, unless the cover of the battery room is adequately protected.
In addition, the above standards also have related warning signs, risk statements and other similar requirements for packaging and instructions, mainly to remind parents and guardians that toy products contain button batteries. Once swallowed, it may cause chemical burns in the body within the shortest two hours, and even death in serious cases; Waste batteries need to be disposed of immediately, and new and used batteries should be kept away from children; If it is suspected that the battery may be swallowed by children or placed in any part of the body, medical help must be sought immediately.
Australian New Consumer Product Standard
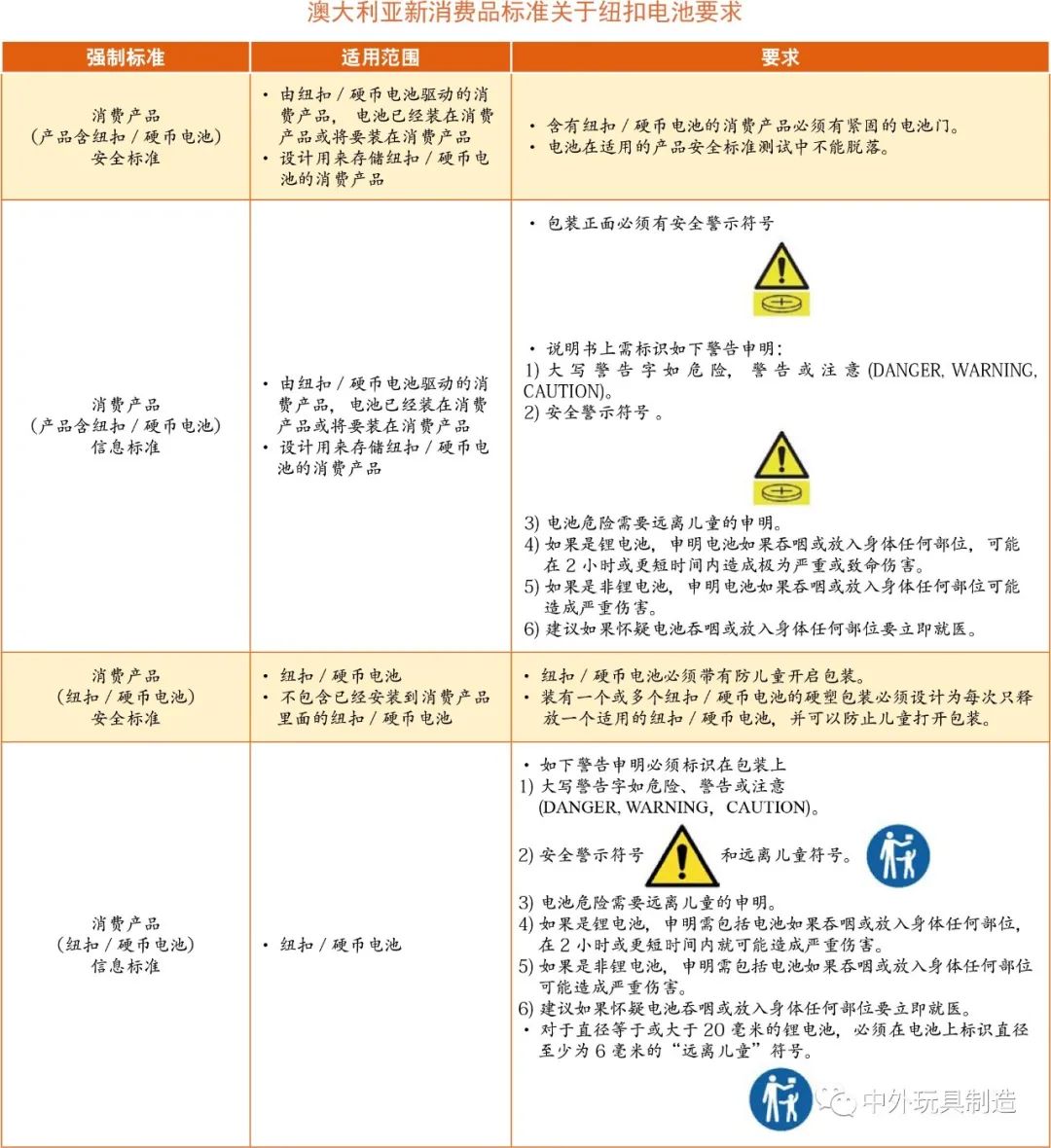
On December 22, 2020, the Australian government officially took effect of the new consumer product standard on the control of button batteries, including four mandatory standards to reduce the risk of casualties caused by the use of button/coin batteries. Mandatory standards include an 18 month transition period. From June 22, 2022, suppliers must meet the requirements of these standards.
 Related Developments
Related Developments
 Solution
Solution